Handles
Abstract

Handles allow the PythonPart user to edit the geometry (and sometimes also other properties) directly in the model view. Common examples are:
- changing a dimension with dimension handle
- define a coordinate with coordinate handle
- execute action with button handle
- hiding or displaying a component with checkbox handle
- increment a dimension with increment handle
- input an angle with rotation handle
A handle is always assigned to at least one PythonPart parameter. It consists if two elements: a handle (the blue circle the user can drag) and an input field. You can show/hide both elements independently.
Definition
Handle as a whole is represented by the class HandleProperties.
Defining a handle means defining following properties:
- Reference point is the anchor of the handle. It's a Point3D
- Handle point is where the handle is located. The calculations are then done based on the vector going from reference point to handle point.
-
Handle type tells, how the handle looks like. All the options are in the enumeration
ElementHandleType. By default a handle is a circle (ElementHandleType.HANDLE_CIRCLE). Following layouts are possible:Layout Type 
HANDLE_ARROW 
HANDLE_CIRCLE 
HANDLE_SQUARE_BLUE 
HANDLE_SQUARE_EMPTY 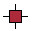
HANDLE_SQUARE_RED 
HANDLE_SQUARE_RIGHT -
Handle parameter data describes the connection between the handle and a parameter. In other words, how the value of the parameter should be calculated, when the handle is moved to a new position. It is represented by the
HandleParameterDataclass. A handle can be connected to multiple parameters, which means that moving it will change the value of all connected parameters (see example coordinate handle). -
Handle direction describes the direction, in which the handle can be moved. The enumeration class
HandleDirectioncontains all the available options
The graph below shows the complete composition of the HandleProperties class.
classDiagram
direction BT
class Point3D {
float X
float Y
float Z
}
class ElementHandleType{
<<Enumeration>>
HANDLE_ARROW
HANDLE_CIRCLE
HANDLE_SQUARE_BLUE
HANDLE_SQUARE_EMPTY
HANDLE_SQUARE_RED
HANDLE_SQUARE_RIGHT
}
class HandleDirection{
<<Enumeration>>
X_DIR
Y_DIR
Z_DIR
XY_DIR
XZ_DIR
YZ_DIR
XYZ_DIR
POINT_DIR
ANGLE
Z_COORD
PLANE_DIR
VECTOR_DIR
CLICK
}
class HandleParameterType{
<<Enumeration>>
X_DISTANCE
Y_DISTANCE
Z_DISTANCE
POINT
POINT_DISTANCE
ANGLE
Z_COORD
VECTOR_DISTANCE
CHECK_BOX
INCREMENT_BUTTON
DECREMENT_BUTTON
}
class HandleParameterData{
<<Dataclass>>
+str param_prop_name
+HandleParameterType param_type
}
class HandleProperties{
+str handle_id
+Point3D handle_point
+Point3D ref_point
+List[HandleParameterData] parameter_data
+HandleDirection handle_move_dir
+ElementHandleType handle_type
}
Point3D --o "2" HandleProperties
ElementHandleType --o "1" HandleProperties
HandleDirection --o "1" HandleProperties
HandleParameterData --o "1..*" HandleProperties
HandleParameterType --o "1" HandleParameterData
Examples
Dimension handle
Let's say we have a simple geometry (a cube), and we want to let the user control a single dimension of it (the height) with a handle. The implementation can look like this:
handle_parameter_data = HandleParameterData("CubeHeight", HandleParameterType.Z_DISTANCE) #(1)!
handle_height = HandleProperties("HeightHandle",
AllplanGeo.Point3D(0,0, build_ele.CubeHeight.value),
AllplanGeo.Point3D(),
[handle_parameter_data], #(2)!
HandleDirection.Z_DIR) #(3)!
handle_list.append(handle_height)
- The handle is connected here to the parameter
CubeHeightwith theZ_DISTANCErecalculation method, meaning that after every handle modification a distance vector between reference point and handle point is calculated and only the Z component is being put back a value to the parameterCubeHeigth. - Here we could let one handle affect several parameters in the property palette, each in a different way.
- The handle should move only in local Z-direction of our PythonPart.
Coordinate handle
Let's say, we want to let the user control the ground view dimensions (length and width) of the PythonPart with a single handle.
handle_parameter_data_list = [HandleParameterData("CubeLength",
HandleParameterType.X_DISTANCE,
False), #(3)!
HandleParameterData("CubeWidth",
HandleParameterType.Y_DISTANCE,
False)] #(1)!
handle_length_width = HandleProperties("LengthWidthHandle",
AllplanGeo.Point3D(build_ele.CubeLength.value,
build_ele.CubeWidth.value,
0),
AllplanGeo.Point3D(),
handle_parameter_data_list,
HandleDirection.XY_DIR)
handle_length_width.info_text = "Ground view dimensions" #(2)!
- Two parameters should be assigned to this handle therefore a list is defined here.
- The string in the optional parameter
info_textwill be displayed ever time the user hovers the handle with the mouse. - Unlike in the first example, the input field in the model view is hidden.
Button handle
Let's say we want the handle to perform some action (mirroring the object). We can place a button in the palette or define a button handle, visible directly in the model view to do that.
<Parameter><!--(1)!-->
<Name>MirrorCuboid</Name>
<Value>False</Value>
<ValueType>CheckBox</ValueType>
</Parameter>
- To be able to temporarily save the mirrored-status of the PythonPart a hidden parameter must be defined. In an Interactor PythonPart we could save this information ex. in a property of the interactor class.
mirror_handle = HandleProperties("MirrorCuboid",
point5,
AllplanGeo.Point3D(),
[], #(1)!
HandleDirection.CLICK) #(2)!
mirror_handle.handle_type = AllplanIFW.ElementHandleType.HANDLE_ARROW
mirror_handle.info_text = "Mirror the cuboid"
mirror_handle.handle_angle = rot_angle #(3)!
handle_list.append(mirror_handle)
- Note that no parameter is assigned to the handle. The handle processing is done
entirely in
move_handle()function by the assigned handle IDMirrorCuboid. - By assigning the handle direction
CLICKthe handle cannot be moved. Themove_handle()is called, when the handle is clicked. - The handle is rotated in XY plane to align with the rotation of the object.
def move_handle(build_ele,
handle_prop: HandleProperties,
input_pnt: AllplanGeo.Point3D,
doc: AllplanEleAdapter.DocumentAdapter):
if handle_prop.handle_id == "MirrorCuboid": #(1)!
build_ele.MirrorCuboid.value = not build_ele.MirrorCuboid.value #(2)!
return create_element(build_ele, doc)
- The name of the handle is stored in the property handle_id
- We use an invisible parameter to temporarily save the mirrored status. The value of the parameter is changed here every time the handle is clicked.
List parameter
Let's say we have a parameter defined as a python list containing Point3D and we want to define a handle for each of these points.
handle_list = []
for index, pnt in enumerate(build_ele.PolyPoints.value): #(2)!
handle_param_data = HandleParameterData("PolyPoints",
HandleParameterType.POINT,
False, #(4)!
list_index = index) #(1)!
handle_list.append(HandleProperties("PolyPoints",
pnt,
AllplanGeo.Point3D(),
[handle_param_data],
HandleDirection.XYZ_DIR))
handle_list[-1].info_text = "Point " + str(index + 1) #(3)!
- As the parameter is defined as list, this argument is now required. The parameter
PolyPointsis a one-dimensional list, therefore thelist_indexis an integer. In case of a two-dimensional list, a list of two integer values must be provided:[index_row, index_column]. - As separate handle must be generated for each point, implementation in a loop is the best solution.
- Here we change the info text for the appended handle.
- We don't want the input fields to be shown for these handles.
Value decrement / increment
Let's say we do not want to allow the user to set a value of a certain parameter (ex. wall thickness) freely, but only increment or decrement it by 100 mm instead.
<Parameter>
<Name>Thickness</Name>
<Text>Thickness</Text>
<Value>1000.</Value>
<ValueType>Length</ValueType>
<MinValue>0</MinValue>
<MaxValue>10000</MaxValue>
<IntervalValue>100</IntervalValue><!--(1)!-->
</Parameter>
- We do want the thickness to increment in 100 mm steps, therefore we also need to constrain the parameter in the property palette separately. Otherwise, the user could change the thickness freely using the palette.
#---------- incrementation handle
increm_handle_param_data = [HandleParameterData("Thickness", #(1)!
HandleParameterType.INCREMENT_BUTTON,
in_decrement_value = 100.)]
increment_handle = HandleProperties(handle_id= "IncrementHandle",
handle_point= point2 + AllplanGeo.Point3D(200, 100, 0),
ref_point= AllplanGeo.Point3D(), #(2)!
handle_param_data= increm_handle_param_data,
handle_move_dir= HandleDirection.CLICK #(3)!
info_text= "Increment thickness by 0.1m")
handle_list.append(increment_handle)
#---------- decrementation handle
decrem_handle_param_data = [HandleParameterData("Thickness", #(4)!
HandleParameterType.DECREMENT_BUTTON,
in_decrement_value = 100.)]
decrement_handle = HandleProperties(handle_id= "DecrementHandle",
handle_point= point2 + AllplanGeo.Point3D(200, -100, 0),
ref_point= AllplanGeo.Point3D(),
handle_param_data= decrem_handle_param_data,
handle_move_dir= HandleDirection.CLICK,
info_text= "Decrement thickness by 0.1m")
decrement_handle.handle_angle = AllplanGeo.Angle(math.pi)
handle_list.append(decrement_handle)
- Defining the handle parameter type this way implies adding the value of 100 mm to the parameter thickness.
- In case of a button handle, this argument is not relevant and can be set to (0,0,0).
- The increment button can be clicked, but not moved. This behaviour is defined here.
- Decrementing a value is a different recaltulation behaviour therefore a separate handle must be defined for that and it must be assigned to the same thickness parameter.
Rotation handle
Let's say we want to allow the user to input an angle (ex. to rotate a geometry) using handle. In this case we need to implement a handle like this:
rot_handle_param_data = HandleParameterData("RotAngleZ",
HandleParameterType.ANGLE) #(1)!
handle_z_rot = HandleProperties(handle_id= "Z_Rotation",
handle_point= poly_points[1], #(2)!
ref_point= poly_points[1], #(3)!
handle_param_data= [rot_handle_param_data],
handle_move_dir= HandleDirection.ANGLE, #(4)!
abs_value= True,
info_text= "Z rotation handle")
handle_z_rot.info_text = "Z rotation handle"
handle_list.append(handle_z_rot)
- This option implies, that an angle value is being calculated
between
handle_pointandref_point - The handle will be drawn in this point.
-
Reference point for the value calculation. The value of the angle will be calculated between the local X-axis with the origin in the
ref_point, and the line going through theref_pointand thehandle_point. This implies a rotation around the local Z-Axis. By default, the directions of the local axes are the same as the global one and can be changed by providing an optional argumentangle_placement, ex. like this: -
A handle can be moved in any direction, just like with
XYZ_DIR, but an arc with arrow will be drawn when hovering with the mouse over the handle to indicate a rotation.
Processing
In standard PythonPart
Creation
In order to create a standard PythonPart with handles, construct one HandleProperties object per each handle and put them in a list:
handle_1 = HandleProperties(...)
handle_2 = HandleProperties(...)
handle_list = [handle_1, handle_2]
Then, assign this list to the handles attribute of the CreateElementResult
object, returned at the end of the create_element() function:
def create_element(build_ele, doc):
...
return CreateElementResult(elements = model_elements_list,
handles = handle_list)
Modification
After every handle modification, the new value of the property must be written back in the property
palette and the element must be recreated. To handle this process, implement the function
move_handle() in your script. Use the
HandlePropertiesService to update the parameter
values
Example
def move_handle(build_ele,
handle_prop: HandleProperties,
input_pnt: NemAll_Python_Geometry.Point3D,
doc: NemAll_Python_IFW_ElementAdapter.DocumentAdapter):
if handle_prop.handle_id == build_ele.MirrorCuboid.name: #(1)!
build_ele.MirrorCuboid.value = not build_ele.MirrorCuboid.value
else:
HandlePropertiesService.update_property_value(build_ele, handle_prop, input_pnt) #(3)!
return create_element(build_ele, doc) #(2)!
- You can process a specific handle (in this case the
MirrorCuboidhandle) differently. as the framework gives the handle name to themove_handle()function. - The PythonPart must be recalculated with every movement of the handle.
- For a standard case you just need to implement this line of code in the
move_handlefunction. The update_property_value method updates the values in the property palette after the handle is modified.
In Script Object
In a script object, handle implementation looks
exactly the same, as in a standard PythonPart (see above), with one exception: instead of
implementing the creation in create_element(), implement it
in the execute().
Processing the event of a handle being moved is done in the move_handle
method of your ScriptObject class. The method is called constantly when the handle is moved (not only once,
when the modification is done). Like in a standard PythonPart, use the
HandlePropertiesService to update the parameter values
of the BuildingElement. At the end, call the
execute method to recalculate the geometry with these
new values:
def move_handle(self,
handle_prop: HandleProperties,
input_pnt : AllplanGeo.Point3D) -> CreateElementResult:
HandlePropertiesService.update_property_value(self.build_ele, handle_prop, input_pnt)
return self.execute()
Example
The complete implementation is shown in the PythonPart Handles, located in:
- ...\Etc\PythonPartsExampleScripts\BasisExamples\General\Handles.py
- ...\Etc\Examples\PythonParts\BasisExamples\General\Handles.pyp
In interactor
In an interactor, each mouse movement and mouse click has to be processed. The same applies
to moving and clicking on a handle. The class for the job is
HandleModificationService.
Here is a typical standard PythonPart workflow:
flowchart TB
start((Start)) --> Placement["PLACEMENT"]
Placement -- "Place PythonPart" --> Input["PARAMETER INPUT"]
Input --"Grab
a handle"--> HandleMod["HANDLE MODIFICATION"]
HandleMod --"Drop a
handle" --> Input
HandleMod --"Press ESC" --> Input
Placement --"Press ESC"--> stop((stop))
Input --"Press ESC"--> stop((stop))
Following instruction will guide you, how to implement it in an interactor and process the handles correctly.
There are three states, in which a PythonPart can find itself: Placement, Parameter input, and handle modification (see enumeration class InteractorInputMode). This is how you should implement these three states and the transition between them:
-
Start: At the very beginning (in the
__init__()) start the HandleModificationService: -
PLACEMENT - now PythonPart follows the mouse cursor. Nothing to do here up to the point, when the user clicks to place the PythonPart. In this moment, handles must be shown. Call
start()to do so:def process_mouse_msg(self, mouse_msg, pnt, msg_info): if self.coord_input.IsMouseMove(mouse_msg): return True # code below this line is executed only when mouse is clicked if self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PLACEMENT: self.handle_modi_service.start(self.handles, #(2)! self.placement_matrix, self.coord_input.GetInputViewDocument(), self.coord_input.GetViewWorldProjection(), True) self.coord_input.InitFirstPointInput(AllplanIFWInput.InputStringConvert("Select handle")) self.input_mode = self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT #(1)! return True- Transition to the state
PARAMETER INPUT - This shows the handles. Here is where you should pass the list of handles. Learn above how to create this list.
- Transition to the state
-
PARAMETER INPUT - now PythonPart is placed in a certain point. It does not follow the mouse any more. The user can input parameter values in the property palette OR grab a handle and move it. The latter must be handled in the
process_mouse_msgmethod as follows:def process_mouse_msg(self, mouse_msg, pnt, msg_info): # handling mouse move if self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PLACEMENT: #(1)! else: handle_grabbed = self.handle_modi_service.process_mouse_msg(mouse_msg, pnt, msg_info) #(2)! if self.coord_input.IsMouseMove(mouse_msg): return True # code below this line is executed only when mouse is clicked if self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PLACEMENT: ... elif self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT and handle_grabbed: self.handle_modi_service.start_new_handle_point_input(self.global_str_table_service) #(3)! self.input_mode = self.InteractorInputMode.HANDLE_MODIFY #(4)! return True- In this mode, no handles are shown so regarding handles there's nothing to do here.
- This call processes the mouse movement. It highlights the handle, when the mouse hovers
over it. When the handle is grabbed, the function will return
True - This call makes the handle "follow" the mouse cursor.
- Transition to the state
HANDLE MODIFY
When at this stage the user presses Esc, the handles need to be destroyed correctly. This must be handled in the
on_cancel_functionby callingstop(), like: -
HANDLE MODIFICATION - now the handle follows the mouse. The user can drop it in a new position by clicking again. This must be handled as follows:
def process_mouse_msg(self, mouse_msg, pnt, msg_info): ... if self.coord_input.IsMouseMove(mouse_msg): return True # code below this line is executed only when mouse is clicked if self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PLACEMENT: ... elif self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT and handle_grabbed: ... elif self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.HANDLE_MODIFY: self.palette_service.update_palette(-1, True) #(1)! self.handle_modi_service.start(self.handles, #(2)! self.placement_matrix, self.coord_input.GetInputViewDocument(), self.coord_input.GetViewWorldProjection(), True) self.input_mode = self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT #(3)! return True- When the handle is dropped, a new parameter value is calculated and must be shown in the palette. Therefore, the palette must be updated.
- The handles must be shown again.
- Transition to the state
PARAMETER INPUT
When at this stage the user presses Esc, the handle should be dropped and the PythonPart must be restored to the initial state (before grabbing the handle), but not terminated! This must be handled in the
on_cancel_function, like:def on_cancel_function(self) -> bool: if self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT: ... elif self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.HANDLE_MODIFY: self.handle_modi_service.reset_value() #(1)! self.handle_modi_service.start(self.handles, self.placement_matrix, self.coord_input.GetInputViewDocument(), self.coord_input.GetViewWorldProjection(), True) self.input_mode = self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT #(2)! return False #(3)!- This resets the parameter values to the state before grabbing the handle
- Transition to the state
PARAMETER_INPUT - After all, PythonPart should continue to run, so return
False.
Modification mode
In the modification mode, the state PLACEMENT
is skipped. What you need to do instead, is to show the handles right away, in the __init__() function:
def __init__(...):
...
if self.modification_element_list.is_modification_element():
self.input_mode = self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT #(1)!
self.handle_modi_service.start(self.handles,
self.placement_matrix,
self.coord_input.GetInputViewDocument(),
self.coord_input.GetViewWorldProjection(),
True)
- Transition to the state
PARAMETER_INPUTright away
Warning
IMPORTANT: Put the above code after showing the palette! Otherwise, the min-max values constraining the handles are not calculated correctly.
Handling special cases
Theoretically, while a handle is grabbed the user can do some input in the property palette.
Confirming the input (pressing Enter) should result in the handle being dropped. You can
handle this in the modify_element_property
as follows:
def modify_element_property(self, page, name, value):
if self.input_mode == self.InteractorInputMode.HANDLE_MODIFY:
self.input_mode = self.InteractorInputMode.PARAMETER_INPUT
The other special case is when the user modifies the handle not by grabbing it, but by
input in the handle's input field. This case is also handled by the
modify_element_property event.
What you must do, is update the palette, since the handle modification may have changed
some of the values. You can implement it as follows:
def modify_element_property(self, page, name, value):
if name == "___SubmitChanges___": #(1)!
self.palette_service.update_palette(-1, True)
return #(2)!
- When a property has been modified using a handle's input field, the name will be like this
- Nothing else to do in this case. You can return from the function at this stage
and place your other interactor logic below this
returnstatement.